Lithium-ion and lithium-iron batteries have very similar names, but they do have some very different properties. This article will show you the similarities and differences between a 100ah lithium-ion battery and a 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery.
Similarities between 100ah lithium ion and 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery
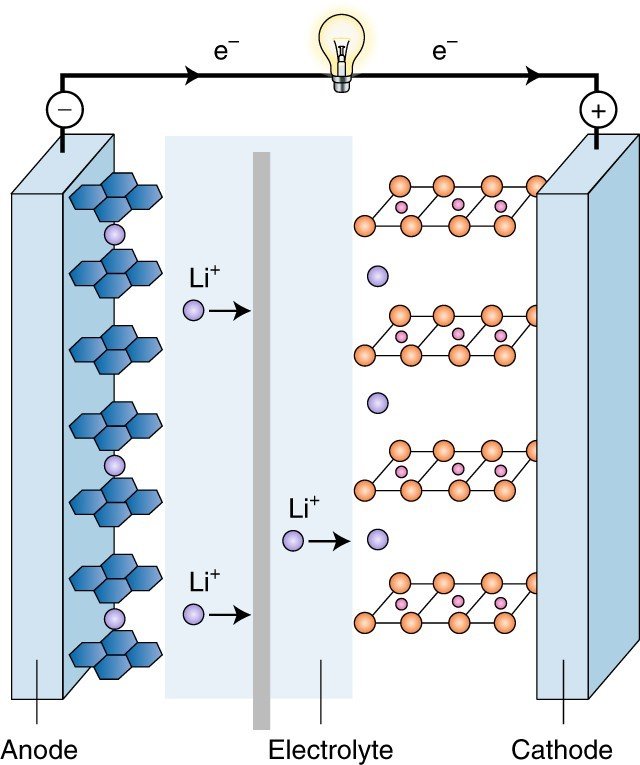
First, both battery types work similarly. The lithium ions in the battery move between the positive and negative electrodes to discharge and charge.
Second, both battery types are rechargeable. Third, they all use a graphite carbon electrode with a metal backing as an anode.
Both types of batteries are applications of fairly new technology in the battery industry. In the past, nickel-based batteries dominated almost the entire battery market. That said, lithium-ion batteries still have room to improve before the technology matures. As a result, they are very expensive at this point and unaffordable for a segment of manufacturers.

The difference between a 100ah lithium-ion battery and a 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery
Despite their common characteristics, 100 ah lithium ion and 100ah lithium iron phosphate batteries are very different in terms of stability, life, and applications.
A. Different chemical composition
First, it’s obvious that by reading their names, you can easily tell that the two types of batteries are made of different materials. Lithium-ion batteries typically use lithium cobaltate (LiCoO2) or lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4) as cathodes. Lithium iron or lithium iron phosphate batteries are usually made of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as a cathode. One thing to note about their raw material is that LiFePO4 is a non-toxic material, while LiCoO2 is inherently harmful. As a result, the disposal of lithium-ion batteries has been a major concern for manufacturers and users.
B. The new technology
Second, lithium-ion batteries are a newer technology than lithium-ion batteries. Phosphate-based technology has better thermal and chemical stability. This means that even if you mishandle a lithium-ion battery, it’s less likely to burn than a lithium-ion battery.
C. Different life cycles
Third, phosphate chemistry provides a longer life cycle. Because both types of batteries are rechargeable, they already have a relatively long life. Lithium-ion batteries last longer because they are more stable when overcharged or short-circuited. On the one hand, lithium-ion batteries have an 80% discharge efficiency and a life span of 13 to 18 years. Its cycle durability is between 400 and 1200. On the other hand, the cycle durability of lithium iron batteries is around 2000.
Which should you choose?
Does that mean 100ah lithium iron phosphate batteries are better than 100ah lithium-ion batteries? The short answer is no, which leads to the fourth difference. Lithium-ion batteries have the highest energy density of any rechargeable battery type on the market. That means charging lithium ions is easier and takes less time. Lithium-ion batteries also have good density, but in general, they are not as powerful as lithium-ion batteries. However, not all batteries are suitable for every use, so a 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery may be better than a 100ah lithium-ion battery for some applications, and vice versa.
Last but not least, a popular application for lithium-ion batteries is in mobile phones and laptops. Apple, for example, makes products that use lithium-ion batteries. It can also be used with power tools such as saws, electric cars, and other portable devices such as cameras, tablets, and even handheld game consoles. Because of their heat resistance and longer life, lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in vehicles, solar lamps, and e-cigarettes. More and more electric car manufacturers are also using lithium-ion batteries.
Performance is the main criterion in choosing the right battery for an application. A 100ah Lithium iron phosphate battery is slightly heavier and larger than a 100ah lithium-ion battery. For this reason, lithium iron is more commonly used in portable devices. The all-new 100ah lithium-ion battery has a higher energy density than the 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery and thus provides better performance for the first few days.
Battery life is defined by the number of charge/discharge cycles a battery can withstand. Some tests have shown that lithium-iron phosphate batteries can last about 2,000 charge/discharge cycles, while lithium-ion batteries may only last 1,000. These tests are done to the point where the battery is significantly reduced, rather than tested to the point of total failure.
The main problem with lithium batteries is their degradation. Over time, lithium-ion batteries will lose capacity and have a total life of 2-3 years. The exact life is a function of usage, the amount of energy released between charges, and other factors such as battery temperature. Compared with lithium-ion batteries, the discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries increases over time.
Long life, slow discharge, and lightweight should be essential features of batteries for everyday use, as a 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery is expected to have a longer “shelf life” than a 100ah lithium-ion battery.
When not in use, the battery should not lose charge at a faster rate. If used after a year or so, it should provide nearly the same performance. This so-called shelf life is about 350 days for lithium iron and 300 days for lithium-ion batteries.
Conclusion:
100ah lithium Ion is not the same as a 100ah lithium Iron phosphate battery. Cobalt is more expensive than iron and phosphate used in lithium iron. As a result, a 100ah lithium iron phosphate battery is less costly to consumers than a 100ah lithium-ion battery (safer materials make them cheaper to manufacture and recycle). Customers can choose as per their application and affordability.

