As grid disruptions become more frequent and prolonged and as attacks on net metering policies increase, it makes increasing sense to combine solar panels and battery storage.
However, the precise number of solar batteries required to power a home? The size of the load you wish to power, the type and size of batteries you’re utilizing, and your energy goals are some of the factors that will determine the response..
This post will discuss the three most popular justifications for purchasing battery storage as well as how to calculate the approximate number of batteries required to meet your energy objectives.
How Many Batteries Are Necessary?
The purpose of your solar batteries will determine how many you need. The majority of people started off wanting to import zero grid electricity.
This ambitious goal of energy storage will, as you’ll soon discover, be prohibitively expensive for the majority of houses.
To start, let’s review the approximate amount of energy storage that a typical Australian home requires.
The typical Australian home uses sixteen kilowatt hours of electricity every day.
You will need a lot more than that, of course, if your home has a large air conditioner, a pool pump, etc.
Given that the majority of Australians work a 9–5 job and are away from home during the day, it is likely that they will use no more than 30% of their electricity during this period. This is because their solar panels will be producing electricity during this time.
That implies that they must purchase the remaining 70% from the grid. In light of this, how many solar batteries are required to cover that 70%?
Calculating the Size of Your Solar Battery Installation
Battery sizes are stated in kilowatt-hours, or kWh, for system sizing purposes.
If a typical home uses 16 kWh, 30 kWh during the day and 70 kWh at night, that equates to roughly 5 kWh during the day and 11 kWh at night.
The average Australian would therefore require roughly 11kWh of solar battery storage to offset all of their nighttime consumption, according to simple math.
As of February 2024, a fully installed Tesla Powerwall 2 with a capacity of 13.5kWh will run you about $15,000. That is presuming a simple installation that incurs no more expenses.
Remember that you don’t have to utilize batteries to make up for all of your nighttime electricity use. If you do the math, the initial kWh of energy storage has the best payback since it works the hardest; when additional kWh are added, the payback lengthens. Therefore, avoid going bankrupt trying to use your batteries to supply every single kilowatt-hour of electricity during the night.
The most crucial factor to keep in mind, though, is that measuring and comparing solar batteries is difficult without a thorough grasp of your energy usage profile. This implies that the first thing you need is a reliable energy monitor with good data for your house.
Then, using their software, a competent installer can precisely calculate how many solar panels and batteries are best for your needs and estimate the payback period. After that, instead of taking a blind plunge into the unknown, you’ll be investing in solar batteries with your eyes wide open.
How Do You Determine How Many Solar Batteries You'll Need?
When you know what you want to do, you can begin figuring out how many batteries your solar system will require.
Honestly, working with a solar.com Energy Advisor to create a personalized system based on your needs, goals, and sun exposure is the simplest and most accurate way to accomplish this. But if you’d like a rough estimate, just follow the instructions below.
Step 1: Determine how much storage you’ll need
Finding your storage needs—that is, the quantity of electricity you require or desire to accomplish your goal or goals—is the first step in determining the number of batteries you will need.
In order to optimize your solar energy savings through load shifting, you need have a minimum amount of storage equal to your electricity consumption during peak hours, which are usually from 4 to 9 pm. The figure below, for instance, illustrates a home’s energy storage requirements. The household uses approximately 9 kWh of electricity between 4 and 9 pm (orange lines) to operate the air conditioner, make supper, and binge-watch Outlander.
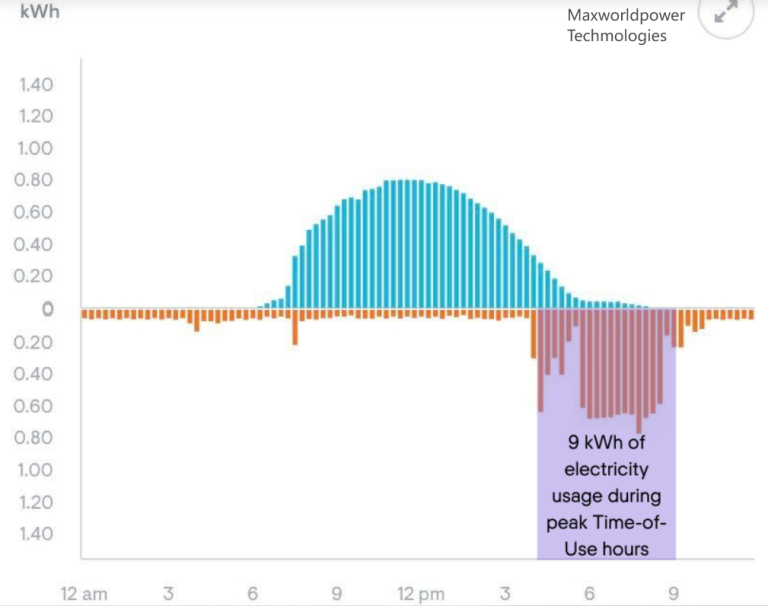
A chart that shows how many batteries a family needs at times of peak consumption
If your goal is to backup important systems or your entire home, you’ll need to do some math to figure out how much storage you’ll need. Choosing what you want to power and how long you want to power it is the aim.
For instance, we calculated in this article that 8 kWh of electricity is needed for a full day’s worth of use to run kitchen appliances, lights, refrigerators, TVs, Wi-Fi, and other electronics, as well as water heating. In order to comfortably run these systems for a day, even in the event of cloudy weather and little solar output, you will need a battery capacity of at least 8 kWh, if not somewhat more just for peace of mind.
If you choose whole-home backup, all you have to do is figure up how much electricity you use on average each day during the season when you’ll probably need backup power. That amount will be your storage requirement.
Step2: Determine the battery size
When you’ve determined how much storage you’ll need, it’s time to go battery shopping.
Batteries can frequently be connected in series to increase storage capacity. For instance, some batteries can be stacked to build battery systems of different sizes. They are available in increments of 3.36 kWh.
Step 3: Set up the batteries to suit your demands for storage
It’s time to set up your system now. In addition, there are other ways to get the system size you want with batteries.
Here are some examples of how to construct a 13 kWh battery system:
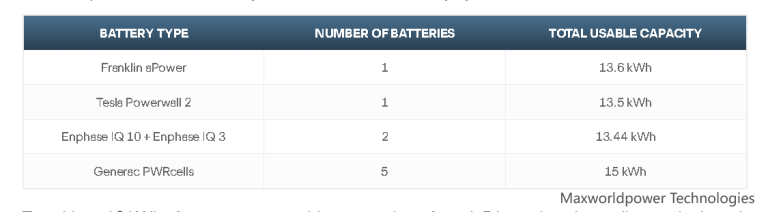
Depending on the manufacturer and type, you could need one to five batteries to reach 13 kWh of storage. Therefore, the precise quantity of batteries required to power a home will rely on the size and type of batteries you select as well as your storage requirements.
Constructing a Unique Battery System
Batteries are quickly turning into a necessary component of cost-effective and robust residential energy systems. The quantity of batteries you require is determined by your energy objectives, storage requirements, and battery type and size selection.
Set objectives and create a solar and battery system that is unique to your house and electricity requirements by working with a solar.com Energy Advisor..
Different Types Of Solar Energy Storage Systems
Solar Storage System Off-Grid
The people making use of this solar storage device are not linked to the electric grid. A sufficient amount of batteries for storage is required for the candidate to operate an off-grid system. The solar system’s building structure needs to be designed to provide year-round power for your house.
Batteries are within the category of chemical energy storage technologies. Chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy by batteries. The batteries’ capacity to contain electrochemical cells makes this possible.
Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System
Grid-tied systems are another name for on-grid storage systems. Instead of using batteries, this system uses a typical grid-tied inverter. The surplus solar energy produced in the home can be exported in return for credits or feed-in tariffs, and homeowners can store some energy on the public utility grid.
Battery Storage Systems for Hybrid Solar Power
Combining two or more energy systems results in a hybrid energy system, the purpose of this solar system is to generate energy. This is an energy-producing system that combines solar and wind technology.
When utilizing this kind of system, the consumer uses the public utility while the solar energy is stored in batteries. When the batteries’ energy is depleted, users can easily transition to the power grid. However, you can also turn to your batteries in the event of a public utility grid power outage.
Sunlight-Based Fuels
The development of this kind of solar energy storage device is still ongoing. At the moment, solar fuel is not widely available in the commercial energy sector. Synthetic compounds manufactured and stored for times when sunshine is scarce include hydrogen, ammonia, and hydrazine. These are known as solar fuels.
A System of Stacked Solar Energy Storage
There are two ways to capture and use solar energy. First, through the use of PV cells, and then through CSP. In conjunction with CSP, a layered energy storage system is used. Solar energy is stored as thermal energy that can be transformed into electricity when needed.
Solar Pools
Additionally, solar ponds combine excellently with systems that use both thermal and concentrated solar power.
Water that gathers and retains solar energy is called a solar pond. A saltwater pond’s bottom water initially warms up when sunshine enters it. As the water loses density, its molecules rise to the surface by convection.
Is It Worth It To Purchase A Solar Battery Bank?
The purpose for which you intend to use the solar batteries will determine how useful they are. In case you want to lower your energy expenses, investing in a solar battery bank can be worthwhile.
During peak energy hours, you can use the energy that you charge your solar battery bank during the day to power your home. Long-term financial savings may result from this. Because solar battery systems run solely on pure, renewable solar energy, they can also assist lessen their impact on the environment.
Depending on your budget and energy requirements, the solar battery system may or may not be a cost-effective alternative because it includes certain upfront fees and continuous maintenance. There are expenses like as battery costs, installation fees, and any required maintenance or repairs.
In the end, it’s critical to conduct thorough research, evaluate your needs and financial situation, and come to a well-informed decision.

